New Lazarus Group Malware Identified: HOPLIGHT
US-CERT recently released a Malware Analysis Report (MAR) identifying a new strain of malware (HOPLIGHT) attributed to the Lazarus Group (HIDDEN COBRA). The joint DHS-FBI report identifies 13 malware samples and 16 IP addresses.
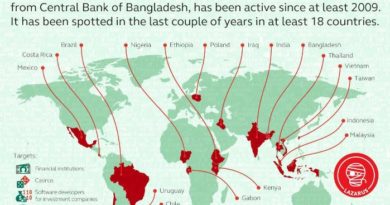
Of the 13 samples, 9 are malicious executables and 4 are files dropped by the executables. The dropped files contain IP addresses and SSL certificates that the samples use for TLS handshake sessions. To facilitate its operations, the Lazarus Group uses compromised C2 servers across the world as illustrated below.
This malware strain is capable of gathering system information, harvesting credentials, connecting to remote hosts, and uploading/downloading files. Also, a DHS Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) official told ZDNet that, “HOPLIGHT has been detected in use globally in a wide array of HIDDEN COBRA malicious activity, not specific to a particular critical infrastructure sector.” Further DHS reports regarding the Lazarus Group can be found on this webpage.
Breakdown of Win32 Malware Samples
The report identifies a malicious Win32 executable (05feed9762bc46b47a7dc5c469add9f163c 16df4ddaafe81983a628da571446) with a compilation date of 5 June 2017. When executed, this sample will collect system information (OS version, volume information, system time) and enumerate system drives and partitions. This sample will attempt a TLS handshake with one of four IP addresses referenced in a data file (udbcgiut.dat) using a public SSL certificate signed by Naver.com. 39 of 66 anti-virus programs used by VirusTotal successfully detected this sample.
The second malicious Win32 sample (2151c1977b4555a1761c12f151969f8e853e26c396fa1a7b74ccbaf3a48f4525) operates similarly to the above sample. It was compiled on 16 May 2017. When executed, the sample will write the ‘udbcgiut.dat’ file to ‘C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Local\Temp’. The sample then attempts outbound SSL connections with the hosts listed in the data file. This sample has a 35 out of 67 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
The third malicious Win32 sample (4c372df691fc699552f81c3d3937729f1dde2a2393f36c92ccc2bd2a033a0818) was compiled on 4 June 2017 and operates similarly to the above samples, except this sample does not drop the ‘udbcgiut.dat’ file. This sample appears to be named ‘lamp.exe’ due to a debug pathway found in the sample: ‘Z:\Develop\41.LampExe\Release\LampExe.pdb’. This sample has a 37 out of 66 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
The fourth malicious Win32 sample (ddea408e178f0412ae78ff5d5adf2439251f68cad4fd853ee466a3c74649642d) also attempts a TLS handshake to the hosts listed in the ‘udbcgiut.dat’ file. This sample was compiled on 6 June 2017. If the sample is unable to establish a connection, the ‘udbcgiut.dat’ file is deleted and an outbound SSL connection is made to 81.94.192[.]10. Additionally, this sample contains APIs associated with Pass-the-Hash (PTH) toolkits, indicating a probable harvesting of user credentials. This sample has a 36 out of 65 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
The fifth malicious Win32 sample (70034b33f59c6698403293cdc28676c7daa8c49031089efa6eefce41e22dccb3) is the oldest, being compiled on 23 August 2016. This sample sets up a service: ‘Network UDP Trace Management Service’. To set up this service, the sample drops a dynamic library, ‘UDPTrcSvc.dll’, into the %System32% directory and adds multiple keys to the registry. The sample then drops two files to the system: ‘udbcgiut.dat’ and ‘MSDFMAPI.INI’. The sample will also attempt the same SLL outbound connections, but does not use any of the SSL certifications. This sample has a 39 out of 65 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
UDBCGIUT.DAT File
The ‘udbcgiut.dat’ file (70902623c9cd0cccc8513850072b70732d02c266c7b7e96d2d5b2ed4f5edc289) is dropped by 3 of the 4 samples listed above. This file will be dropped in ‘%AppData%\Local\Temp’ for 32bit executables and ‘C:\Windows’ for 64bit executables. The four IP addresses encoded in this sample are as follows:
- 197.211.212[.]59:443 (Service provider in Zimbabwe)
- 181.39.135[.]126:443 (Service provider in Ecuador)
- 11.175.92[.]57:7443 (DOD NIC in Ohio)
- 81.94.192[.]147:7443 (IaaS provider in UK)
This sample has a 0 out of 48 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
Win64 Malware Sample
The report identifies this Win64 sample (12480585e08855109c5972e85d99cda7701fe992bc1754f1a0736f1eebcb004d) that was compiled on 6 June 2017. This variant hooks the Windows Local Security Authority (lsass.exe), which checks the registry for the data value ‘rdpproto’ in the ‘SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa’ registry key and adds it if missing. Next, the sample will drop the embedded ‘rdpproto.dll’ into the ‘%System32% directory, and write the ‘udbcgiut.dat’ file to ‘C:\Windows’. The sample then attempts SSL outbound connections to the listed hosts as outlined above. This sample has a 35 out of 72 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
Dynamic Library Lists
The ‘rdpproto.dll’ sample (49757cf85657757704656c079785c072bbc233cab942418d99d1f63d43f28359) was also compiled on 6 June 2017. This sample is dropped into the ‘%System32%’ directory and will attempt to send SSL Client Hello packets to the following embedded IP addresses:
- 21.252.107[.]198 (DOD NIC)
- 70.224.36[.]194 (AT&T private address, Texas)
- 113.114.117[.]122 (Chinese service provider, Guandong)
- 47.206.4[.]145 (ISP in New York)
- 84.49.242[.]125 (ISP in Norway)
- 26.165.218[.]44 (DOD NIC)
- 137.139.135[.]151 (SUNY in NY)
- 97.90.44[.]200 (ISP in Missouri)
- 128.200.115[.]228 (UC Irvine in CA)
- 186.169.2[.]237 (ISP in Colombia)
This sample has a 40 out of 71 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
The report also identifies a malicious Win64 dynamic library (4a74a9fd40b63218f7504f806fce71dffefc1b1d6ca4bbaadd720b6a89d47761) called ‘Vote_Controller.dll’ that was also compiled on 6 June 2017. This sample has the same functionality as the DLL above and uses the same Naver SSL certificate. Additionally, the company name associated with this sample is ‘Kamsky Co, Ltd.’ This sample has a 22 out of 71 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
The next malicious Win64 dynamic library (83228075a604e955d59edc760e4c4ed16eedabfc8f6ac291cf21b4fcbcd1f70a) was compiled on 16 May 2017 and is similar to the ‘Vote_Controller.dll’ above. However, this sample uses the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) process to recompile the MOF files in the WMI repository. These MOF files are compiled by the OS when a specific event takes place and may be used to run commands and establish persistency on the system. Consequently, the sample modifies the ‘HKLM\Software\WBEM\WDM’ registry key, which is also used by VMWare Tools. Thus, VMWare Tools will no longer work, which may be an attempt to block malware analysis in a VMWare sandbox environment. Also, this sample has a 21 out of 64 detection ratio on VirusTotal.
The ‘UDPTrcSvc.dll’ (cd5ff67ff773cc60c98c35f9e9d514b597cbd148789547ba152ba67bfc0fec8f) Win32 library was compiled on 23 August 2016. This service will attempt to modify the system firewall (‘cmd.exe /c netsh firewall add portopening TCP 0 “adp”‘), which makes the system allow incoming connections and function as a proxy server. This is similar to previous Lazarus Group threat activity.
Configuration File
The MSDFMAPI.INI (96a296d224f285c67bee93c30f8a309157f0daa35dc5b87e410b78630a09cfc7) file is written to ‘C:\WINDOWS and to ‘%UserProfile\APpData\Local\VirtualStore\Windows%’. This sample was referenced in an AlienVault pulse posted nearly a year ago associated with APT 33, which is an Iranian-backed threat actor that has targeted Saudi and ROK petrochemical companies. Additionally, this sample is associated with a 12 February 2018 PDF phishing scam and a malicious PDF purported to come from the shipping company Maersk. Furthermore, the file is found in multiple PDF samples.
Password Protected Sample
The final sample (d77fdabe17cdba62a8e728cbe6c740e2c2e541072501f77988674e07a05dfb39) also contains a public SSL certificate signed by Naver, but the payload for this file is protected by a password or a key. This sample has a 2 out of 60 detection ratio on VirusTotal.